Subject Alternative Name (SAN) Extension
The Subject Alternative Name (SAN) is an X.509 v3 certificate extension that binds additional information to the subject DN of this certificate.
The most notable information includes:
- DNS Name
- RFC822 Name
DNS Name
CA uses this construct when issuing SSL server certificates. It contains the domain(s) for which this certificate is issued.
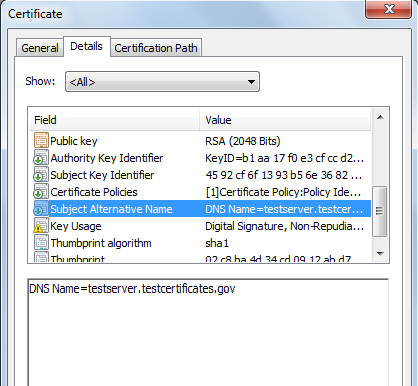
In the above certificate, the SAN extension is selected which further contains the DNS Name. The value of DNS Name shows the domain whom this certificate is issued. There can be multiple occurrences of DNS Name in a SAN extension.
There are different types of SSL certificates offered by public certification authorities e.g.
- Single domain SSL certificates
- Multiple domains SSL certificates
- Multiple sub domains SSL certificates
- Wild card SSL certificates
- OV SSL certificates (To be discussed later)
- EV SSL certificates (To be discussed later)
In all of the above types of certificates offered by different public certification authorities, apart from the certificate policy/vetting procedure, the difference is the values in the DNS Name under the SAN extension.
In single domain SSL certificates, there would be only one value of DNS Name in the SAN extension as shown below.

In multiple domains SSL certificates, there would be at least two domains present under the SAN extension as shown below.

In multiple sub domains SSL certificates, there would be multiple sub domains present under the SAN extension as shown below.

In the wild card certificate, It is possible to add unlimited domains or sub domains e.g.

In the above wild card certificate, the accepted domain names would be www.test.com, blog.test.com, web.test.com and so on.
The benefit of multiple domains, sub domains or wild card certificates is that one has to buy only a single certificate.
When this SSL server certificate is presented to the browser and if the domain from where the certificate is downloaded is the one present in the DNS Name of this certificate then the certificate is accepted by the browser otherwise a warning is issued by the browser.
RFC822 Name
It contains an email address of the user whom this certificate is issued. This construct can be present in the document signing, email signing, SSL client authentication certificates etc.
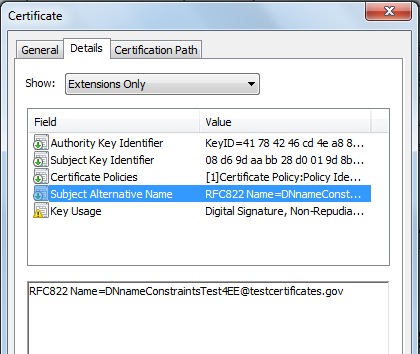
In the above certificate, SAN extension is selected which further contains the RFC822Name. The value of the RFC822Name contains an email address whom this certificate is issued.